Waterproof cables refer to a type of cable in which waterproof sheath materials and designs are adopted in the cable structure to prevent water from entering the interior of the cable structure. Its main purpose is to ensure the long-term safe and stable operation of the cable in damp, underground or underwater and other high-humidity environments, and to prevent problems such as electrical breakdown and insulation aging caused by water intrusion. According to their different protection methods, they can be classified into waterproof cables that prevent water from entering by relying on the structure itself, and water-blocking cables that prevent water from spreading through material reactions.
Introduction to JHS Type Waterproof Cable
The JHS type waterproof cable is a common rubber-sheathed waterproof cable. Both its insulation layer and sheath are made of rubber, featuring excellent flexibility and water tightness. It is widely used in environments such as submersible pump power supply, underground operations, underwater construction, and power station drainage, and is suitable for long-term or repetitive movement in water. This type of cable usually adopts a three-core structure and is suitable for most water pump connection scenarios. As its appearance is similar to that of ordinary rubber-sheathed cables, when selecting the type, it is particularly necessary to confirm whether it has an internal waterproof structure or a metal sheath design to ensure that it meets the actual needs of the usage environment.
The structure and protection methods of waterproof cables
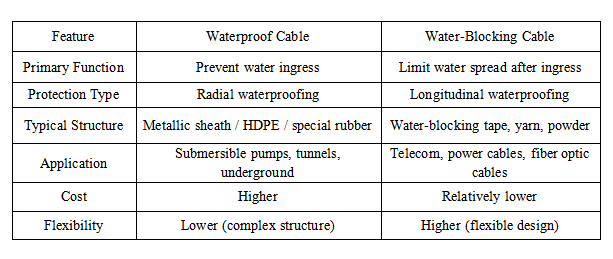
The structural design of waterproof cables usually varies according to the usage scenarios and voltage levels. For single-core waterproof cables, semi-conductive water-blocking tape or ordinary water-blocking tape is often wrapped around the insulation shielding layer, and additional water-blocking materials can be set outside the metal shielding layer. At the same time, water-blocking powder or water-blocking filling ropes are combined to enhance the overall sealing performance. The sheath material is mostly high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or special rubber with water-blocking performance, which is used to enhance the overall radial waterproof capacity.
For multi-core or medium and high voltage cables, to enhance waterproof performance, plastic coated aluminum tape is often longitudinally wrapped inside the inner lining layer or sheath, while HDPE sheath is extruded on the outer layer to form a composite waterproof structure. For cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) insulated cables of 110kV and above grades, metal sheaths such as hot-pressed aluminum, hot-pressed lead, welded corrugated aluminum, or cold-drawn metal sheaths are often used to provide better radial protection capabilities.
The protection mechanism of waterproof cables: longitudinal and radial waterproofing
The waterproofing methods of waterproof cables can be divided into longitudinal waterproofing and radial waterproofing. Longitudinal waterproofing mainly relies on water-blocking materials, such as water-blocking powder, water-blocking yarn, and water-blocking tape. After water enters, they will rapidly expand to form a physical isolation layer, effectively preventing water from spreading along the length of the cable. Radial waterproofing mainly prevents water from seeping radially into the cable from the outside through sheath materials or metal sheaths. High-grade waterproof cables usually combine the use of two mechanisms to achieve comprehensive water-tight protection.


The difference between waterproof cables and water-blocking cables
Although the purposes of the two are similar, there are obvious differences in structural principles and application scenarios. The key point of waterproof cables is to prevent water from entering the interior of the cables. Their structure mostly adopts metal sheaths or high-density sheath materials, emphasizing radial waterproofing. They are suitable for long-term submerged environments such as submersible pumps, underground equipment, and damp tunnels. Water-blocking cables, on the other hand, focus more on how to restrict the diffusion of water after it enters. They mainly use water-blocking materials that expand upon contact with water, such as water-blocking powder, water-blocking yarn, and water-blocking tape, to achieve longitudinal water-blocking effects. They are commonly used in application scenarios such as communication cables, power cables, and optical cables. The overall structure of waterproof cables is more complex and the cost is relatively higher, while water-blocking cables have a flexible structure and controllable cost, and are suitable for a wide range of laying environments.
Introduction to Water-Blocking Structure Forms (for Water-blocking Cables)
Water-blocking structures can be classified into conductor water-blocking structures and core water-blocking structures according to the internal position of the cable. The water-blocking structure of conductors involves adding water-blocking powder or water-blocking yarn during the twisting process of conductors to form a longitudinal water barrier layer. It is suitable for situations where it is necessary to prevent the diffusion within the conductors. The water-blocking structure of the cable core adds water-blocking tape inside the cable core. When the sheath is damaged and water enters, it rapidly expands and blocks the cable core channels, preventing further spread. For multi-core structures, it is recommended to adopt independent water-blocking designs for each core respectively to make up for the water-blocking blind areas caused by the large gaps and irregular shapes of the cable cores, thereby enhancing the overall waterproof reliability.
Comparison Table of Waterproof Cables and Water-blocking Cables (English Version)
Conclusion
Waterproof cables and water-blocking cables each have their own technical characteristics and clear application scopes. In actual engineering, the most suitable waterproof structure scheme should be comprehensively evaluated and selected based on the laying environment, service life, voltage level and mechanical performance requirements. At the same time, while emphasizing the performance of cables, attention should also be paid to the quality and compatibility of waterproof raw materials.
ONE WORLD is dedicated to providing cable manufacturers with complete waterproof and water-blocking material solutions, including water-blocking tape, semi-conductive water-blocking tape, water-blocking yarn, HDPE, cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), etc., covering multiple fields such as communication, optical cables, and power. We not only offer high-quality materials, but also have a professional technical team to support customers in designing and optimizing various waterproof structures, helping to enhance the reliability and performance of cables.
If you need further information on product parameters or sample applications, please feel free to contact the ONE WORLD team.
Post time: May-16-2025