Currently, communication technology has become an indispensable part of modern ships. Whether used for navigation, communication, entertainment, or other critical systems, reliable signal transmission is the foundation for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of vessels. Marine coaxial cables, as an important communication transmission medium, play a vital role in ship communication systems due to their unique structure and excellent performance. This article will provide a detailed introduction to the structure of marine coaxial cables, aiming to help you better understand their design principles and application advantages.
Basic Structure Introduction
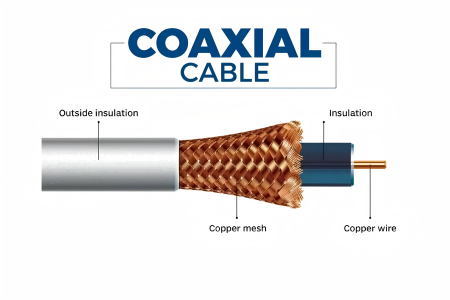
Inner Conductor
The inner conductor is the core component of marine coaxial cables, primarily responsible for transmitting signals. Its performance directly affects the efficiency and quality of signal transmission. In ship communication systems, the inner conductor carries the task of transmitting signals from transmitting equipment to receiving equipment, making its stability and reliability crucial.
The inner conductor is typically made of high-purity copper. Copper has excellent conductive properties, ensuring minimal signal loss during transmission. Additionally, copper possesses good mechanical properties, enabling it to withstand certain mechanical stresses. In some special applications, the inner conductor may be silver-plated copper to further enhance conductive performance. Silver-plated copper combines the conductive properties of copper with the low-resistance characteristics of silver, delivering outstanding performance in high-frequency signal transmission.
The manufacturing process of the inner conductor includes copper wire drawing and plating treatment. Copper wire drawing requires precise control of wire diameter to ensure the conductive performance of the inner conductor. Plating treatment can improve the corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of the inner conductor. For more demanding applications, the inner conductor may employ multi-layer plating technology to further enhance performance. For example, a multi-layer plating of copper, nickel, and silver provides better conductivity and corrosion resistance.
The diameter and shape of the inner conductor significantly impact the transmission performance of coaxial cables. For marine coaxial cables, the diameter of the inner conductor usually needs to be optimized based on specific transmission requirements to ensure stable transmission in marine environments. For instance, high-frequency signal transmission requires a thinner inner conductor to reduce signal attenuation, while low-frequency signal transmission can use a thicker inner conductor to improve signal strength.
Insulation Layer
The insulation layer is located between the inner conductor and the outer conductor. Its primary function is to prevent signal leakage and short circuits, isolating the inner conductor from the outer conductor. The material of the insulation layer must have excellent electrical insulation and mechanical properties to ensure the stability and integrity of signals during transmission.
The insulation layer of marine coaxial cables must also possess salt spray corrosion resistance to meet the special requirements of marine environments. Common insulation materials include foam polyethylene (Foam PE), polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), polyethylene (PE), and polypropylene (PP). These materials not only have excellent insulation properties but can also withstand certain temperature variations and chemical corrosion.
The thickness, uniformity, and concentricity of the insulation layer significantly impact the cable’s transmission performance. The insulation layer must be thick enough to prevent signal leakage but not excessively thick, as this would increase cable weight and cost. Additionally, the insulation layer must have good flexibility to accommodate cable bending and vibration.
Outer Conductor (Shielding Layer)
The outer conductor, or shielding layer of the coaxial cable, primarily serves to shield against external electromagnetic interference, ensuring signal stability during transmission. The design of the outer conductor must consider anti-electromagnetic interference and anti-vibration performance to guarantee signal stability during ship navigation.
The outer conductor is typically made of metal braided wire, which offers excellent flexibility and shielding performance, effectively reducing electromagnetic interference. The braiding process of the outer conductor requires precise control of braid density and angle to ensure shielding performance. After braiding, the outer conductor undergoes heat treatment to improve its mechanical and conductive properties.
Shielding effectiveness is a key metric for evaluating the performance of the outer conductor. Higher shielding attenuation indicates better anti-electromagnetic interference performance. Marine coaxial cables require high shielding attenuation to ensure stable signal transmission in complex electromagnetic environments. Additionally, the outer conductor must have good flexibility and anti-vibration properties to adapt to the mechanical environment of ships.
To enhance anti-electromagnetic interference performance, marine coaxial cables often employ double-shielded or triple-shielded structures. A double-shielded structure includes a layer of metal braided wire and a layer of aluminum foil, effectively reducing the impact of external electromagnetic interference on signal transmission. This structure performs exceptionally well in complex electromagnetic environments, such as ship radar systems and satellite communication systems.
Sheath
The sheath is the protective layer of the coaxial cable, shielding the cable from external environmental erosion. For marine coaxial cables, sheath materials must possess properties such as salt spray corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and flame retardancy to ensure reliability and safety in harsh environments.
Common sheath materials include low-smoke zero-halogen (LSZH) polyolefin, polyurethane (PU), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polyethylene (PE). These materials protect the cable from external environmental erosion. LSZH materials do not produce toxic smoke when burned, meeting the safety and environmental protection standards commonly required in marine environments. To enhance ship safety, marine coaxial cable sheath materials typically use LSZH, which not only reduces harm to crew during fires but also minimizes environmental pollution.
Special Structures
Armored Layer
In applications requiring additional mechanical protection, an armored layer is added to the structure. The armored layer is usually made of steel wire or steel tape, effectively improving the cable’s mechanical properties and preventing damage in harsh environments. For example, in ship chain lockers or on decks, armored coaxial cables can withstand mechanical impacts and abrasion, ensuring stable signal transmission.
Waterproof Layer
Due to the high humidity of marine environments, marine coaxial cables often incorporate a waterproof layer to prevent moisture penetration and ensure stable signal transmission. This layer typically includes water-blocking tape or water-blocking yarn, which swell upon contact with moisture to effectively seal the cable structure. For additional protection, a PE or XLPE jacket may also be applied to enhance both waterproofing and mechanical durability.
Summary
The structural design and material selection of marine coaxial cables are key to their ability to transmit signals stably and reliably in harsh marine environments. Each component works together to form an efficient and stable signal transmission system. Through various structural optimization designs, marine coaxial cables meet the stringent requirements of signal transmission.
With the continuous development of ship communication technology, marine coaxial cables will continue to play a vital role in ship radar systems, satellite communication systems, navigation systems, and entertainment systems, providing strong support for the safe and efficient operation of vessels.
About ONE WORLD
ONE WORLD is committed to providing high-quality cable raw materials for the production of various marine cables. We supply key materials such as LSZH compounds, foam PE insulation materials, silver-plated copper wires, plastic coated aluminum tapes, and metal braided wires, supporting customers in achieving performance requirements like corrosion resistance, flame retardancy, and durability. Our products comply with REACH and RoHS environmental standards, offering reliable material guarantees for ship communication systems.
Post time: Jun-30-2025