Aramid fiber, short for aromatic polyamide fiber, is listed among the four high-performance fibers prioritized for development in China, along with carbon fiber, ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber (UHMWPE), and basalt fiber. Like ordinary nylon, aramid fiber belongs to the family of polyamide fibers, with amide bonds in the main molecular chain. The key difference lies in the bonding: nylon’s amide bonds are connected to aliphatic groups, whereas aramid’s are conjugated with benzene rings. This special molecular structure gives aramid fiber extremely high axial strength (>20cN/dtex) and modulus (>500GPa), making it the preferred material for reinforcing high-end cables.
Types of Aramid Fiber
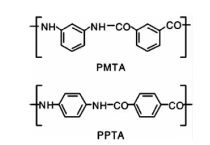
Aramid fiber mainly includes wholly aromatic polyamide fibers and heterocyclic aromatic polyamide fibers, which can be further categorized into ortho-aramid, para-aramid (PPTA), and meta-aramid (PMTA). Among these, meta-aramid and para-aramid are the ones that have been industrialized. From a molecular structure perspective, the main difference between these two lies in the position of the carbon atom in the benzene ring to which the amide bond is attached. This structural difference leads to significant distinctions in mechanical properties and thermal stability.
Para-Aramid
Para-aramid, or poly(p-phenylene terephthalamide) (PPTA), also known in China as Aramid 1414, is a linear high polymer with more than 85% of its amide bonds directly linked to aromatic rings. The most commercially successful para-aramid products are DuPont’s Kevlar® and Teijin’s Twaron®, which dominate the global market. It was the first fiber ever produced using a liquid crystalline polymer spinning solution, ushering in a new era of high-performance synthetic fibers. In terms of mechanical properties, its tensile strength can reach 3.0–3.6 GPa, elastic modulus 70–170 GPa, and elongation at break 2–4%. These exceptional characteristics give it irreplaceable advantages in optical cable reinforcement, ballistic protection, and other fields.
Meta-Aramid
Meta-aramid, or poly(m-phenylene isophthalamide) (PMTA), also known in China as Aramid 1313, is a leading high-temperature-resistant organic fiber. Its molecular structure consists of amide groups linking meta-phenylene rings, forming a zigzag linear chain stabilized by strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds in a 3D network. This structure endows the fiber with excellent flame retardancy, thermal stability, and radiation resistance. A typical product is DuPont’s Nomex®, with a Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) of 28–32, a glass transition temperature of about 275°C, and continuous service temperature above 200°C, making it widely used in fire-resistant cables and high-temperature insulation materials.
Outstanding Properties of Aramid Fiber
Aramid fiber offers ultra-high strength, high modulus, heat resistance, acid and alkali resistance, low weight, insulation, aging resistance, long life cycle, chemical stability, no molten droplets during combustion, and non-toxic gas emissions. From a cable application perspective, para-aramid outperforms meta-aramid in thermal resistance, with a continuous service temperature range of -196 to 204°C and no decomposition or melting at 500°C. Para-aramid’s most notable properties include ultra-high strength, high modulus, heat resistance, chemical resistance, and low density. Its strength exceeds 25 g/dtex—5 to 6 times that of high-quality steel, 3 times that of fiberglass, and twice that of high-strength nylon industrial yarn. Its modulus is 2–3 times that of steel or fiberglass and 10 times that of high-strength nylon. It is twice as tough as steel wire and weighs only about 1/5 as much, making it particularly well-suited for use as reinforcement in optical cables, submarine cables, and other high-end cable types.
Mechanical Properties of Aramid Fiber
Meta-aramid is a flexible polymer with breaking strength higher than ordinary polyester, cotton, or nylon. It has a high elongation rate, soft hand feel, good spinnability, and can be produced into short fibers or filaments of varying denier. It can be spun into fabrics and nonwovens using standard textile machinery and processed to meet the protective apparel needs of various industries. In electrical insulation, meta-aramid’s flame-retardant and heat-resistant properties stand out. With an LOI greater than 28, it will not continue to burn after leaving the flame. Its flame resistance is intrinsic to its chemical structure, making it permanently flame-retardant—resistant to performance loss due to washing or long-term use. Meta-aramid has excellent thermal stability, with continuous use at 205°C and strong retention of strength even at temperatures above 205°C. Its decomposition temperature is high, and it does not melt or drip at high temperatures, only beginning to carbonize above 370°C. These properties make it ideal for insulation and reinforcement in high-temperature or fire-resistant cables.
Chemical Stability of Aramid Fiber
Meta-aramid has excellent resistance to most chemicals and concentrated inorganic acids, although it is sensitive to concentrated sulfuric and nitric acids. It also has good alkali resistance at room temperature.
Radiation Resistance of Aramid Fiber
Meta-aramid exhibits exceptional radiation resistance. For example, under prolonged exposure to 1.2×10⁻² W/cm² ultraviolet light and 1.72×10⁸ rad gamma rays, its strength remains unchanged. This outstanding radiation resistance makes it especially suitable for cables used in nuclear power stations and spacecraft.
Durability of Aramid Fiber
Meta-aramid also shows excellent abrasion and chemical resistance. After 100 washes, fabric made from domestically produced meta-aramid retains over 85% of its original tear strength. In cable applications, this durability ensures long-term mechanical and electrical performance stability.
Applications of Aramid Fiber
Aramid fiber is widely used in China’s aerospace, automotive, electromechanical, construction, and sports industries due to its excellent mechanical properties, high-temperature resistance, and chemical stability. It is regarded as a key material for the future development of high-performance industries. In particular, aramid plays an irreplaceable role in the fields of communication optical cables, power cables, high-temperature-resistant cables, submarine cables, and specialty cables.
Aerospace and Military Fields
Aramid fiber features low density, high strength, and excellent corrosion resistance. It is widely applied in structural components of aerospace vehicles, such as rocket motor casings and broadband radome structures. Its composite materials exhibit excellent impact resistance and electromagnetic wave transparency, significantly reducing aircraft weight and enhancing safety. In the defense sector, aramid is used in bulletproof vests, helmets, and blast-resistant containers, making it a leading material for the next generation of lightweight military protection.
Construction and Transportation Fields
In the construction industry, aramid fiber is used for structural reinforcement and bridge cable systems due to its lightweight, flexibility, and corrosion resistance. It is especially effective in reinforcing irregular structures. In transportation, aramid is applied in tire cord fabrics for automobiles and aircraft. Aramid-reinforced tires offer high strength, puncture resistance, heat resistance, and long service life, meeting the performance demands of modern high-speed vehicles and aircraft.
Electrical, Electronics, and Cable Industry
Aramid fiber has particularly prominent applications in the electrical, electronics, and wire & cable manufacturing sectors, especially in the following areas:
Tensile Members in Optical Cables: With high tensile strength and modulus, aramid fiber serves as the tensile member in communication optical cables, protecting delicate optical fibers from deformation under tension and ensuring stable signal transmission.
Reinforcement in Cables: In specialty cables, submarine cables, power cables, and high-temperature-resistant cables, aramid is commonly used as a central reinforcement element or armor layer. Compared to metal reinforcements, aramid offers superior strength at a lower weight, greatly enhancing cable tensile strength and mechanical stability.
Insulation and Flame Retardancy: Aramid composites possess excellent dielectric and thermal stability. They are widely used in cable insulation layers, flame-retardant jackets, and halogen-free low-smoke sheathing. Aramid paper, after being impregnated with insulating varnish, is combined with natural mica for use in high-temperature-resistant motors and transformers.
Fire-Resistant and Rail Transit Cables: Aramid fiber’s inherent flame resistance and heat tolerance make it ideal for use in shipboard cables, rail transit cables, and nuclear-grade fire-resistant cables, where safety standards are stringent.
EMC and Lightweighting: Aramid’s excellent electromagnetic transparency and low dielectric constant make it suitable for EMI shielding layers, radar radomes, and optoelectronic integration components, helping to improve electromagnetic compatibility and reduce system weight.
Other Applications
Due to its high aromatic ring content, aramid fiber offers outstanding chemical stability and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for marine ropes, oil drilling cables, and overhead transmission optical cables in harsh environments. It is also widely used in premium sports equipment, protective gear, and automotive brake pads, and is increasingly being adopted as an environmentally friendly alternative to asbestos in sealing and insulation applications, thermal insulation panels, and other sealing components, ensuring both performance and environmental safety.
Post time: Jul-31-2025